Macromechanics of a Laminate. Textbook: Mechanics of Composite Materials Author: Autar Kaw
|
|
|
- Ἀλαλά Παπάγος
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Macromechanics of a Laminate Tetboo: Mechanics of Composite Materials Author: Autar Kaw
2 Figure 4.1 Fiber Direction θ z
3 CHAPTER OJECTIVES Understand the code for laminate stacing sequence Develop relationships of mechanical and hgrothermal loads applied to a laminate to strains and stresses in each lamina Find the elastic stiffnesses of laminate based on the elastic moduli of individual laminas and the stacing sequence Find the coefficients of thermal and moisture epansion of a laminate based on elastic moduli, coefficients of thermal and moisture epansion of individual laminas, and stacing sequence
4 Laminate ehavior elastic moduli the stacing position thicness angles of orientation coefficients of thermal epansion coefficients of moisture epansion
5 P P z (a M M z (b M M P P (c z Figure 4.
6 Figure 4. z z M M N M N N M N (a (b
7 Classical Lamination Theor Each lamina is orthotropic. Each lamina is homogeneous. A line straight and perpendicular to the middle surface remains straight and perpendicular to the middle surface during deformation. ( γz = γz =. The laminate is thin and is loaded onl in its plane (plane stress ( σz = τz = τz =. Displacements are continuous and small throughout the laminate ( u, v, w << h, where h is the laminate thicness. Each lamina is elastic. No slip occurs between the lamina interfaces.
8 Figure 4.4 U h/ Mid-Plane z h/ z A A α α w o zα Cross-Section efore Loading Cross-Section after Loading
9 Global Strains in a Laminate. w w w + z v + u v u = γ ε ε. κ κ κ + z γ ε ε =
10 Figure 4.5 Mid-Plane z Laminate Strain Variation Stress Variation
11 Figure 4.6 h 1 h 1 h/ h h Mid-Plane h h -1 t h/ z h n h n-1 n
12 Stresses in a Lamina in a Laminate γ ε ε = τ σ σ κ κ κ + z γ ε ε =
13 Forces and Stresses dz, τ σ σ = N N N h/ -h/ dz, τ σ σ = N N N h h n = - 1 1
14 Forces and Strains dz γ ε ε = N N N h h n = z dz κ κ κ + h h n =
15 Forces and Strains γ ε ε h h n = 1 dz = N N N - 1 κ κ κ h h n = 1 z dz + 1
16 Integrating terms h h h h dz = ( h h - 1, 1 1 zdz = ( h h -,
17 Forces and Strains N N N A = A A 11 A A A A A A 66 ε ε + γ κ κ κ n A ij - = 1 = [( ] ( h - h, i = 1,, 6; j = 1,, 6, ij 1 1 n = ij [( ] ( h - h ij - 1 = 1, i = 1,, 6; j = 1,, 6
18 Moments and Strains κ κ κ D D D D D D D D D + γ ε ε = M M M ,, ; j =,, i = h - h ( ] [( = D - ij n = ij
19 Forces, Moments, Strains, Curvatures κ κ κ γ ε ε D D D D D D D D D A A A A A A A A A = M M M N N N
20 Steps 1. Find the value of the reduced stiffness matri [] for each pl using its four elastic moduli, E 1, E, v, G in Equation (.9.. Find the value of the transformed reduced stiffness matri [ ] for each pl using the [] matri calculated in Step 1 and the angle of the pl in Equation (.14 or Equations (.17 and (.18.. Knowing the thicness, t of each pl, find the coordinate of the top and bottom surface, h i, i = 1, , n of each pl using Equation ( Use the [ ] matrices from Step and the location of each pl from Step to find the three stiffness matrices [A], [] and [D] from Equation ( Substitute the stiffness matri values found in Step 4 and the applied forces and moments in Equation (4.9.
21 Steps 6. Solve the si simultaneous Equations (4.9 to find the midplane strains and curvatures. 7. Knowing the location of each pl, find the global strains in each pl using Equation ( For finding the global stresses, use the stress-strain Equation ( For finding the local strains, use the transformation Equation ( For finding the local stresses, use the transformation Equation (.94.
22 Figure 4.7 z = -7.5mm z = -.5mm z =.5mm z = 7.5mm o o -45 o z 5mm 5mm 5mm
23 Problem A [//-45] Graphite/Epo laminate is subjected to a load of N = N = 1 N/m. Use the unidirectional properties from Table.1 of Graphite/Epo. Assume each lamina has a thicness of 5 mm. Find athe three stiffness matrices [A], [] and [D] for a three pl [//-45] Graphite/Epo laminate. bmid-plane strains and curvatures. cglobal and local stresses on top surface of pl. dpercentage of load N taen b each pl.
24 Solution A From Eample.4, the reduced stiffness matri for the Graphite/Epo pl is [] = ( Pa
25 From Equation (.99, the transformed reduced stiffness matri for each of the three plies are [ ] = (1 Pa [ ] = (1 Pa = ( [ ] -45 Pa
26 The total thicness of the laminate is h = (.5( =.15 m. The mid plane is.75 m from the top and bottom of the laminate. Hence using Equation (4., the location of the pl surfaces are h = -.75 m h 1 = -.5 m h =.5 m h =.75 m
27 From Equation (4.8a, the etensional stiffness matri [A] is Aij = [ ] (h - h -1 =1 ij [A] = (1 [(-.5 - (-.75] (1 [.5 - (-.5] (1 [ ] 46.59
28 The [A] matri [A] = 1.79(1.884(1 5.66( (1 4.5( ( ( ( (1 Pa - m
29 From Equation (4.8b, the coupling stiffness matri [] is h - (h [ ] 1 = 1 - ij =1 ij ] ( [(-.5 ( [] = 9 [ ] (-.5 - (.5 ( ] (.5 - [(.75 (
30 The Matri ( 6 ( 5 ( ( 5. ( 6. ( ( 6. ( 6. ( [] = Pa- m 17. 1
31 From Equation (4.8c, the bending stiffness matri [D] is D ij [D] = + 1 = 1 1 = [ ij ] (h - h -1 ( ( 1 9 (. 5 - ( [( (-. ] [ ] ( [( (. ] 1 9 5
32 The [D] matri [D] = ( 4 ( ( ( ( 9. 1 ( ( ( ( Pa - m
33 Since the applied load is N = N = 1N/m, the midplane strains and curvatures can be found b solving the following set of simultaneous linear equations (Equation ( (1 N (1 = M 6 -.9(1 M (1 M 6-1.7( ( ( ( ( ( (1 5.66( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1.4( (1-5.4( ( ( ( (1 9.( ( ( ( (1-5.4( (1 7.66(1 ε ε γ κ κ κ
34 1/m 4.11(1.85( (1 m/m 7.598(1 -.49(1.(1 = κ κ κ γ ε ε Mid-plane strains and curvatures
35 C The strains and stresses at the top surface of the pl are found as follows. First, the top surface of the pl is located at z = h 1 = -.5 m. From Equation (4., ε ε γ, top.(1 =.49( ( ( (1 -.85(1 4.11( (1 = 4.1( ( m/m
36 Table 4.1 Global strains (m/m in Eample 4. Pl # Position ε ε γ 1 ( Top Middle ottom ( (1-7.8 ( ( ( ( ( ( (1-6 ( Top Middle ottom.8 (1-7. ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1-7 (-45 Top Middle ottom.866 ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1-6. (1-6
37 Using the stress-strain Equations (.98 for an angle pl, σ σ τ, top = (1 9.8(1 4.1( ( (1 = 7.91(1.81( Pa
38 Table 4. Global stresses (Pa in Eample 4. Pl # Position σ σ τ 1 ( Top Middle ottom.51 ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1 4 ( Top Middle ottom 6.9 ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1 4 (-45 Top Middle ottom 1.5 ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1 4
39 The local strains and local stress as in the pl at the top surface are found using transformation Equation (.94 as γ ε1 ε / = ( ( (1 / ε1 ε γ = 4. 87( (1. 66( m/m
40 Table 4. Local strains (m/m in Eample 4. Pl # Position ε 1 ε γ 1 ( Top Middle ottom ( (1-7.8 ( ( ( ( ( ( (1-6 ( Top Middle ottom 4.87( ( ( (1-6.( (1-6.66(1-6.74( (1-6 (-45 Top Middle ottom 1.96( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1-7
41 .81(1 7.91(1 6.9( = τ σ σ Pa 1.89(1 4.48(1 9.97(1 = 4 4 4
42 Table 4.4 Local stresses (Pa in Eample 4. Pl # Position σ 1 σ τ 1 ( Top Middle ottom.51 ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (1 4 ( Top Middle ottom 9.97 ( (1 5.7 ( ( ( ( ( ( (1 4 (-45 Top Middle ottom.586 ( ( (1 4. (1 4.1 ( ( ( (1 -.5 (1
43 D The portion of the load N taen b each pl can be calculated b integrating the stress through the thicness of each pl. However, since the stress varies linearl through each pl, the portion of the load N taen is simpl the product of the stress σ at the middle of each pl (See Table 4. and the thicness of the pl. Portion of load N taen b pl = 4.464(1 4 (5(1 - =. N/m Portion of load N taen b pl = 1.6(1 5 (5(1 - = 51.5 N/m Portion of load N taen b -45 pl = 4.9(1 4 (5(1 - = 45. N/m The sum total of the loads shared b each pl is 1 N/m, ( which is the applied load in the -direction, N. σ
44 Percentage of load N taen b pl. = 1 1 =. % Percentage of load N taen b pl 51.5 = 1 1 = 5.15 % Percentage of load N taen b -45 pl 45. = 1 1 = 4.5 %
45 Figure 4.8 Strip 1, E 1, ν 1 Strip, E, ν
Chapter 7 Transformations of Stress and Strain
 Chapter 7 Transformations of Stress and Strain INTRODUCTION Transformation of Plane Stress Mohr s Circle for Plane Stress Application of Mohr s Circle to 3D Analsis 90 60 60 0 0 50 90 Introduction 7-1
Chapter 7 Transformations of Stress and Strain INTRODUCTION Transformation of Plane Stress Mohr s Circle for Plane Stress Application of Mohr s Circle to 3D Analsis 90 60 60 0 0 50 90 Introduction 7-1
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
= l. = l. (Hooke s Law) Tensile: Poisson s ratio. σ = Εε. τ = G γ. Relationships between Stress and Strain
 Relationships between tress and train (Hooke s Law) When strains are small, most of materials are linear elastic. Tensile: Ε hear: Poisson s ratio Δl l Δl l Nominal lateral strain (transverse strain) Poisson
Relationships between tress and train (Hooke s Law) When strains are small, most of materials are linear elastic. Tensile: Ε hear: Poisson s ratio Δl l Δl l Nominal lateral strain (transverse strain) Poisson
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Lecture 6 Mohr s Circle for Plane Stress
 P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsk HT08 Lecture 6 Mohr s Circle for Plane Stress Transformation equations for plane stress. Procedure for constructing Mohr s circle. Stresses on an inclined element.
P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsk HT08 Lecture 6 Mohr s Circle for Plane Stress Transformation equations for plane stress. Procedure for constructing Mohr s circle. Stresses on an inclined element.
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Matrices Review. Here is an example of matrices multiplication for a 3x3 matrix
 Matrices Review Matri Multiplication : When the number of columns of the first matri is the same as the number of rows in the second matri then matri multiplication can be performed. Here is an eample
Matrices Review Matri Multiplication : When the number of columns of the first matri is the same as the number of rows in the second matri then matri multiplication can be performed. Here is an eample
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Stresses in a Plane. Mohr s Circle. Cross Section thru Body. MET 210W Mohr s Circle 1. Some parts experience normal stresses in
 ME 10W E. Evans Stresses in a Plane Some parts eperience normal stresses in two directions. hese tpes of problems are called Plane Stress or Biaial Stress Cross Section thru Bod z angent and normal to
ME 10W E. Evans Stresses in a Plane Some parts eperience normal stresses in two directions. hese tpes of problems are called Plane Stress or Biaial Stress Cross Section thru Bod z angent and normal to
Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACEG
 Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS
 VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
Radiation Stress Concerned with the force (or momentum flux) exerted on the right hand side of a plane by water on the left hand side of the plane.
 upplement on Radiation tress and Wave etup/et down Radiation tress oncerned wit te force (or momentum flu) eerted on te rit and side of a plane water on te left and side of te plane. plane z "Radiation
upplement on Radiation tress and Wave etup/et down Radiation tress oncerned wit te force (or momentum flu) eerted on te rit and side of a plane water on te left and side of te plane. plane z "Radiation
CYLINDRICAL & SPHERICAL COORDINATES
 CYLINDRICAL & SPHERICAL COORDINATES Here we eamine two of the more popular alternative -dimensional coordinate sstems to the rectangular coordinate sstem. First recall the basis of the Rectangular Coordinate
CYLINDRICAL & SPHERICAL COORDINATES Here we eamine two of the more popular alternative -dimensional coordinate sstems to the rectangular coordinate sstem. First recall the basis of the Rectangular Coordinate
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
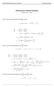 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Section 8.2 Graphs of Polar Equations
 Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Introduction to Theory of. Elasticity. Kengo Nakajima Summer
 Introduction to Theor of lasticit Summer Kengo Nakajima Technical & Scientific Computing I (48-7) Seminar on Computer Science (48-4) elast Theor of lasticit Target Stress Governing quations elast 3 Theor
Introduction to Theor of lasticit Summer Kengo Nakajima Technical & Scientific Computing I (48-7) Seminar on Computer Science (48-4) elast Theor of lasticit Target Stress Governing quations elast 3 Theor
Review Test 3. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact value of the expression. 1) sin - 11π 1 1) + - + - - ) sin 11π 1 ) ( -
Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact value of the expression. 1) sin - 11π 1 1) + - + - - ) sin 11π 1 ) ( -
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
ΕΒ ΟΜΑ ΙΑΙΟ ΩΡΟΛΟΓΙΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ Α ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟΥ 2012-2013
 ΕΒ ΟΜΑ ΙΑΙΟ ΩΡΟΛΟΓΙΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ Α ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟΥ 2012-2013 Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Π. Αγγελίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Π. Αγγελίδης-,Β Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Π. Αγγελίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Π. Αγγελίδης-,Β
ΕΒ ΟΜΑ ΙΑΙΟ ΩΡΟΛΟΓΙΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ Α ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟΥ 2012-2013 Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Π. Αγγελίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Π. Αγγελίδης-,Β Θ. Ζυγκιρίδης- Π. Αγγελίδης- Μ. Λούτα- Π. Αγγελίδης-,Β
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2
![If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2 If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2](/thumbs/53/31933086.jpg) Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Mechanics of Materials Lab
 Mechanics of Materials Lab Lecture 9 Strain and lasticity Textbook: Mechanical Behavior of Materials Sec. 6.6, 5.3, 5.4 Jiangyu Li Jiangyu Li, Prof. M.. Tuttle Strain: Fundamental Definitions "Strain"
Mechanics of Materials Lab Lecture 9 Strain and lasticity Textbook: Mechanical Behavior of Materials Sec. 6.6, 5.3, 5.4 Jiangyu Li Jiangyu Li, Prof. M.. Tuttle Strain: Fundamental Definitions "Strain"
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΑΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΩΤΕΡΑΣ ΠΡΟΣΘΕΤΙΚΗΣ
 ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΑΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΩΤΕΡΑΣ ΠΡΟΣΘΕΤΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΤΙΚΗ ΜΕΛΕΤΗ ΤΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΑΤΗΤΙΚΗΣ ΙΚΑΝΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΟΡΙΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΠΡΟΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΑΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΣΥΝΔΕΣΜΩΝ ΑΚΡΙΒΕΙΑΣ
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΑΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΟΔΟΝΤΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΩΤΕΡΑΣ ΠΡΟΣΘΕΤΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΤΙΚΗ ΜΕΛΕΤΗ ΤΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΑΤΗΤΙΚΗΣ ΙΚΑΝΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΟΡΙΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΠΡΟΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΑΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΣΥΝΔΕΣΜΩΝ ΑΚΡΙΒΕΙΑΣ
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π 2, π 2
 Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
θ) Ο αριθμός των εγκύρων ψηφοδελτίων που έλαβε κάθε ένας συνδυασμός ή μεμονωμένος υποψήφιος ανέρχεται:
 θ) Ο αριθμός των εγκύρων ψηφοδελτίων που έλαβε κάθε ένας συνδυασμός ή μεμονωμένος υποψήφιος ανέρχεται: 6 7 8 9 0 ΝΕΑ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΣΥΝΑΣΠΙΣΜΟΣ ΡΙΖΟΣΠΑΣΤΙΚΗΣ ΑΡΙΣΤΕΡΑΣ ΠΑΝΕΛΛΗΝΙΟ ΣΟΣΙΑΛΙΣΤΙΚΟ ΚΙΝΗΜΑ (ΠΑ.ΣΟ.Κ)
θ) Ο αριθμός των εγκύρων ψηφοδελτίων που έλαβε κάθε ένας συνδυασμός ή μεμονωμένος υποψήφιος ανέρχεται: 6 7 8 9 0 ΝΕΑ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΣΥΝΑΣΠΙΣΜΟΣ ΡΙΖΟΣΠΑΣΤΙΚΗΣ ΑΡΙΣΤΕΡΑΣ ΠΑΝΕΛΛΗΝΙΟ ΣΟΣΙΑΛΙΣΤΙΚΟ ΚΙΝΗΜΑ (ΠΑ.ΣΟ.Κ)
DETERMINATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENT
 EXPERIMENT 5 DETERMINATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENT Purpose: Determine μ k, the kinetic coefficient of friction and μ s, the static friction coefficient by sliding block down that acts as an inclined plane.
EXPERIMENT 5 DETERMINATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENT Purpose: Determine μ k, the kinetic coefficient of friction and μ s, the static friction coefficient by sliding block down that acts as an inclined plane.
( ) 2 and compare to M.
 Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1
![[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1 [1] P Q. Fig. 3.1](/thumbs/79/80362156.jpg) 1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
2. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν.
 Experiental Copetition: 14 July 011 Proble Page 1 of. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν. Ένα μικρό σωματίδιο μάζας (μπάλα) βρίσκεται σε σταθερή απόσταση z από το πάνω μέρος ενός
Experiental Copetition: 14 July 011 Proble Page 1 of. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν. Ένα μικρό σωματίδιο μάζας (μπάλα) βρίσκεται σε σταθερή απόσταση z από το πάνω μέρος ενός
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (2, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = 1+9 = 3.
 Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com June 2005 1. A car of mass 1200 kg moves along a straight horizontal road. The resistance to motion of the car from non-gravitational forces is of constant magnitude 600 N. The
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com June 2005 1. A car of mass 1200 kg moves along a straight horizontal road. The resistance to motion of the car from non-gravitational forces is of constant magnitude 600 N. The
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Linearized Lifting Surface Theory Thin-Wing Theory
 13.021 Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 23 Copright c 2001 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 23 Linearized Lifting Surface Theor Thin-Wing Theor
13.021 Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 23 Copright c 2001 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 23 Linearized Lifting Surface Theor Thin-Wing Theor
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Tube : beam model : analytical
 TUBES Tube : beam model : analytical Tube = simply supported homogeneous & isotropic beam Load = point load (man) & distributed load (wind) z a L I x = 1 [ BH 3 bh 3] ; I z = 1 [ HB 3 hb 3] 12 12 F y x
TUBES Tube : beam model : analytical Tube = simply supported homogeneous & isotropic beam Load = point load (man) & distributed load (wind) z a L I x = 1 [ BH 3 bh 3] ; I z = 1 [ HB 3 hb 3] 12 12 F y x
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) April 26, 2017.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
E T E L. E e E s G LT. M x, M y, M xy M H N H N x, N y, N xy. S ijkl. V v V crit
 A c,a f,a m E c.e f,e m E e E s G f,g m L M x, M y, M xy M H N H N x, N y, N xy P c,p f,p m Q S S ijkl T T V V v V crit W h k t c,t f,t m u 0 v c,v f,v m w c,w f,w m cross-sectional area of composite,fiber
A c,a f,a m E c.e f,e m E e E s G f,g m L M x, M y, M xy M H N H N x, N y, N xy P c,p f,p m Q S S ijkl T T V V v V crit W h k t c,t f,t m u 0 v c,v f,v m w c,w f,w m cross-sectional area of composite,fiber
Aerodynamics & Aeroelasticity: Beam Theory
 Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο National Technical Universit of thens erodnamics & eroelasticit: Beam Theor Σπύρος Βουτσινάς / Spros Voutsinas Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης
Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο National Technical Universit of thens erodnamics & eroelasticit: Beam Theor Σπύρος Βουτσινάς / Spros Voutsinas Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης
ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2
 ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
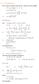 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
1. Sketch the ground reactions on the diagram and write the following equations (in units of kips and feet). (8 points) ΣF x = 0 = ΣF y = 0 =
 IDE S8 Test 6 Name:. Sketch the ground reactions on the diagram and write the following equations (in units of kips and feet). (8 points) ΣF x = = ΣF y = = ΣM A = = (counter-clockwise as positie). Sketch
IDE S8 Test 6 Name:. Sketch the ground reactions on the diagram and write the following equations (in units of kips and feet). (8 points) ΣF x = = ΣF y = = ΣM A = = (counter-clockwise as positie). Sketch
Συνυπογράφουν αλφαβητικά:
 Συνυπογράφουν αλφαβητικά: Κλαίρη Αβραμίδου Κίκα Αγαμέμνωνος Jill Αγαπητού Άγης Αγαπίου Γιώργος Αγαπίου Ανδρέας Αγγελίδης Έρικ Αγγελίδης Οδυσσέας Αγγελίδης Σίμος Αγγελίδης Στέλλα Αγγελίδη Ελένη Αδαμίδου
Συνυπογράφουν αλφαβητικά: Κλαίρη Αβραμίδου Κίκα Αγαμέμνωνος Jill Αγαπητού Άγης Αγαπίου Γιώργος Αγαπίου Ανδρέας Αγγελίδης Έρικ Αγγελίδης Οδυσσέας Αγγελίδης Σίμος Αγγελίδης Στέλλα Αγγελίδη Ελένη Αδαμίδου
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Lecture 5 Plane Stress Transformation Equations
 Lecture 5 Plane Stress Transformation Equations Stress elements and plane stress. Stresses on inclined sections. Transformation equations. Principal stresses, angles, and planes. Maimum shear stress. Normal
Lecture 5 Plane Stress Transformation Equations Stress elements and plane stress. Stresses on inclined sections. Transformation equations. Principal stresses, angles, and planes. Maimum shear stress. Normal
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS! Simple Tension Test! The Stress-Strain Diagram! Stress-Strain Behavior of Ductile and Brittle Materials! Hooke s Law! Strain Energy! Poisson s Ratio! The Shear Stress-Strain
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS! Simple Tension Test! The Stress-Strain Diagram! Stress-Strain Behavior of Ductile and Brittle Materials! Hooke s Law! Strain Energy! Poisson s Ratio! The Shear Stress-Strain
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
10.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response)
 Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
ΕΠΙΤΥΧΟΝΤΕΣ ΑΕΙ 2009 Αρχιτεκτόνων Μηχανικών Κρήτης
 ΕΠΙΤΥΧΟΝΤΕΣ ΑΕΙ 2009 Χρηστίδης Δ. Ανωγιάτη Χ. Κοκκολάκη Α. Λουράντου Α. Χασάπης Φ. Σταυροπούλου Ε. Αλωνιστιώτη Δ. Καρκασίνας Α. Μαραγκουδάκης Θ. Κεφαλάς Γ. Μπαχά Α. Μπέζα Γ. Μποραζέλης Ν. Χίνης Π. Λύτρα
ΕΠΙΤΥΧΟΝΤΕΣ ΑΕΙ 2009 Χρηστίδης Δ. Ανωγιάτη Χ. Κοκκολάκη Α. Λουράντου Α. Χασάπης Φ. Σταυροπούλου Ε. Αλωνιστιώτη Δ. Καρκασίνας Α. Μαραγκουδάκης Θ. Κεφαλάς Γ. Μπαχά Α. Μπέζα Γ. Μποραζέλης Ν. Χίνης Π. Λύτρα
Tutorial problem set 6,
 GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
ΠΣΤΧΛΑΚΘ ΕΡΓΑΛΑ ΜΕΣΡΘΕΛ ΟΠΣΛΚΟΤ ΒΑΚΟΤ ΑΣΜΟΦΑΛΡΑ ΜΕ ΘΛΛΑΚΟ ΦΩΣΟΜΕΣΡΟ ΕΚΟ
 ln(f( )) ΑΡΛΣΟΣΕΛΕΛΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΛΣΘΜΛΟ ΚΕΑΛΟΝΛΚΘ ΣΜΘΜΑ ΦΤΛΚΘ ΠΣΤΧΛΑΚΘ ΕΡΓΑΛΑ ΜΕΣΡΘΕΛ ΟΠΣΛΚΟΤ ΒΑΚΟΤ ΑΣΜΟΦΑΛΡΑ ΜΕ ΘΛΛΑΚΟ ΦΩΣΟΜΕΣΡΟ ΕΚΟ 4,6 4,4 4,2 4,0 3,8 3,6 3,4 3,2 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1 2 3 4 5
ln(f( )) ΑΡΛΣΟΣΕΛΕΛΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΛΣΘΜΛΟ ΚΕΑΛΟΝΛΚΘ ΣΜΘΜΑ ΦΤΛΚΘ ΠΣΤΧΛΑΚΘ ΕΡΓΑΛΑ ΜΕΣΡΘΕΛ ΟΠΣΛΚΟΤ ΒΑΚΟΤ ΑΣΜΟΦΑΛΡΑ ΜΕ ΘΛΛΑΚΟ ΦΩΣΟΜΕΣΡΟ ΕΚΟ 4,6 4,4 4,2 4,0 3,8 3,6 3,4 3,2 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1 2 3 4 5
Spherical Coordinates
 Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Ingenieurbüro Frank Blasek - Beratender Ingenieur Am Kohlhof 10, Osterholz-Scharmbeck Tel: 04791/ Fax: 04791/
 Page: 10 CONTENTS Contents... 10 General Data... 10 Structural Data des... 10 erials... 10 Sections... 10 ents... 11 Supports... 11 Loads General Data... 12 LC 1 - Vollast 120 km/h 0,694 kn/qm... 12 LC,
Page: 10 CONTENTS Contents... 10 General Data... 10 Structural Data des... 10 erials... 10 Sections... 10 ents... 11 Supports... 11 Loads General Data... 12 LC 1 - Vollast 120 km/h 0,694 kn/qm... 12 LC,
Ingenieurbüro Frank Blasek - Beratender Ingenieur Am Kohlhof 10, Osterholz-Scharmbeck Tel: 04791/ Fax: 04791/
 Page: 1 CONTENTS Contents... 1 General Data... 1 Structural Data des... 1 erials... 1 Sections... 1 ents... 2 Supports... 2 Loads General Data... 3 LC 1 - Vollast 90 km/h 0,39 kn/qm... 3 LC, LG Results
Page: 1 CONTENTS Contents... 1 General Data... 1 Structural Data des... 1 erials... 1 Sections... 1 ents... 2 Supports... 2 Loads General Data... 3 LC 1 - Vollast 90 km/h 0,39 kn/qm... 3 LC, LG Results
Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom
 Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
ΑΚΑΓΗΜΙΑ ΔΜΠΟΡΙΚΟΤ ΝΑΤΣΙΚΟΤ ΜΑΚΔΓΟΝΙΑ ΥΟΛΗ ΜΗΥΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ
 ΑΚΑΓΗΜΙΑ ΔΜΠΟΡΙΚΟΤ ΝΑΤΣΙΚΟΤ ΜΑΚΔΓΟΝΙΑ ΥΟΛΗ ΜΗΥΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ ΘΔΜΑ: Μειέηε θαη θαηαζθεπή κεηαηξνπέα DC DC γηα ην εξγαζηήξην ειεθηξηθώλ κεραλώλ. ΠΟΤΓΑΣΔ :Βαιαβαλίδεο Υξήζηνο Δπζηαζίνπ Βαζίιεηνο ΔΠΙΒΛΔΠΩΝ
ΑΚΑΓΗΜΙΑ ΔΜΠΟΡΙΚΟΤ ΝΑΤΣΙΚΟΤ ΜΑΚΔΓΟΝΙΑ ΥΟΛΗ ΜΗΥΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ ΘΔΜΑ: Μειέηε θαη θαηαζθεπή κεηαηξνπέα DC DC γηα ην εξγαζηήξην ειεθηξηθώλ κεραλώλ. ΠΟΤΓΑΣΔ :Βαιαβαλίδεο Υξήζηνο Δπζηαζίνπ Βαζίιεηνο ΔΠΙΒΛΔΠΩΝ
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΜΟΡΦΩΣΕΩΝ ΧΑΛΥΒ ΙΝΩΝ ΦΟΡΕΩΝ ΜΕΓΑΛΟΥ ΑΝΟΙΓΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΥΠΟΥ MBSN ΜΕ ΤΗ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ ΙΩΝ: ΠΡΟΤΑΣΗ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗΣ ΣΕ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΟ ΣΤΕΓΑΣΤΡΟ
 ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΜΟΡΦΩΣΕΩΝ ΧΑΛΥΒ ΙΝΩΝ ΦΟΡΕΩΝ ΜΕΓΑΛΟΥ ΑΝΟΙΓΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΥΠΟΥ MBSN ΜΕ ΤΗ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ ΙΩΝ: ΠΡΟΤΑΣΗ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗΣ ΣΕ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΟ ΣΤΕΓΑΣΤΡΟ Νικόλαος Αντωνίου Πολιτικός Μηχανικός Τµήµα Πολιτικών Μηχανικών, Α.Π.Θ.,
ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΜΟΡΦΩΣΕΩΝ ΧΑΛΥΒ ΙΝΩΝ ΦΟΡΕΩΝ ΜΕΓΑΛΟΥ ΑΝΟΙΓΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΥΠΟΥ MBSN ΜΕ ΤΗ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ ΙΩΝ: ΠΡΟΤΑΣΗ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗΣ ΣΕ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΟ ΣΤΕΓΑΣΤΡΟ Νικόλαος Αντωνίου Πολιτικός Μηχανικός Τµήµα Πολιτικών Μηχανικών, Α.Π.Θ.,
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
The logic of the Mechanics of Materials
 Torsion The logic of the Mechanics of Materials Torsion Chapter 5 Torsion Torsional failures (ductile, buckling, buckling): Bars subjected to Torsion Let us now consider a straight bar supported at one
Torsion The logic of the Mechanics of Materials Torsion Chapter 5 Torsion Torsional failures (ductile, buckling, buckling): Bars subjected to Torsion Let us now consider a straight bar supported at one
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Quadratic Expressions
 Quadratic Expressions. The standard form of a quadratic equation is ax + bx + c = 0 where a, b, c R and a 0. The roots of ax + bx + c = 0 are b ± b a 4ac. 3. For the equation ax +bx+c = 0, sum of the roots
Quadratic Expressions. The standard form of a quadratic equation is ax + bx + c = 0 where a, b, c R and a 0. The roots of ax + bx + c = 0 are b ± b a 4ac. 3. For the equation ax +bx+c = 0, sum of the roots
2012-2013 Πειραιάς:25/2/2013
 ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΔΙΔΑΣΚΑΛΙΑΣ (ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟ: 2) ΣΑΜΑΘ04-ΑΠΕΙΡΟΣΤΙΚΟΣ ΛΟΓΙΣΜΟΣ ΙΙ 08:15 08:15-11:00, 203 08:15-10:00, 203 ΣΑΜΑΘ21-1-ΠΙΘΑΝΟΤΗΤΕΣ Ι (ΤΜΗΜΑ Α:Α-Λ) 13:15 13:15-16:00, 203 ΑΝΤΖΟΥΛΑΚΟΣ Δ. ΑΝΤΖΟΥΛΑΚΟΣ Δ. ΣΑΜΑΘ21-1-ΠΙΘΑΝΟΤΗΤΕΣ
ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΔΙΔΑΣΚΑΛΙΑΣ (ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟ: 2) ΣΑΜΑΘ04-ΑΠΕΙΡΟΣΤΙΚΟΣ ΛΟΓΙΣΜΟΣ ΙΙ 08:15 08:15-11:00, 203 08:15-10:00, 203 ΣΑΜΑΘ21-1-ΠΙΘΑΝΟΤΗΤΕΣ Ι (ΤΜΗΜΑ Α:Α-Λ) 13:15 13:15-16:00, 203 ΑΝΤΖΟΥΛΑΚΟΣ Δ. ΑΝΤΖΟΥΛΑΚΟΣ Δ. ΣΑΜΑΘ21-1-ΠΙΘΑΝΟΤΗΤΕΣ
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής
 Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
Lecture 8 Plane Strain and Measurement of Strain
 P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsk HT08 Lecture 8 Plane Strain and Measurement of Strain Plane stress versus plane strain. Transformation equations. Principal strains and maimum shear strains. Mohr
P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsk HT08 Lecture 8 Plane Strain and Measurement of Strain Plane stress versus plane strain. Transformation equations. Principal strains and maimum shear strains. Mohr
